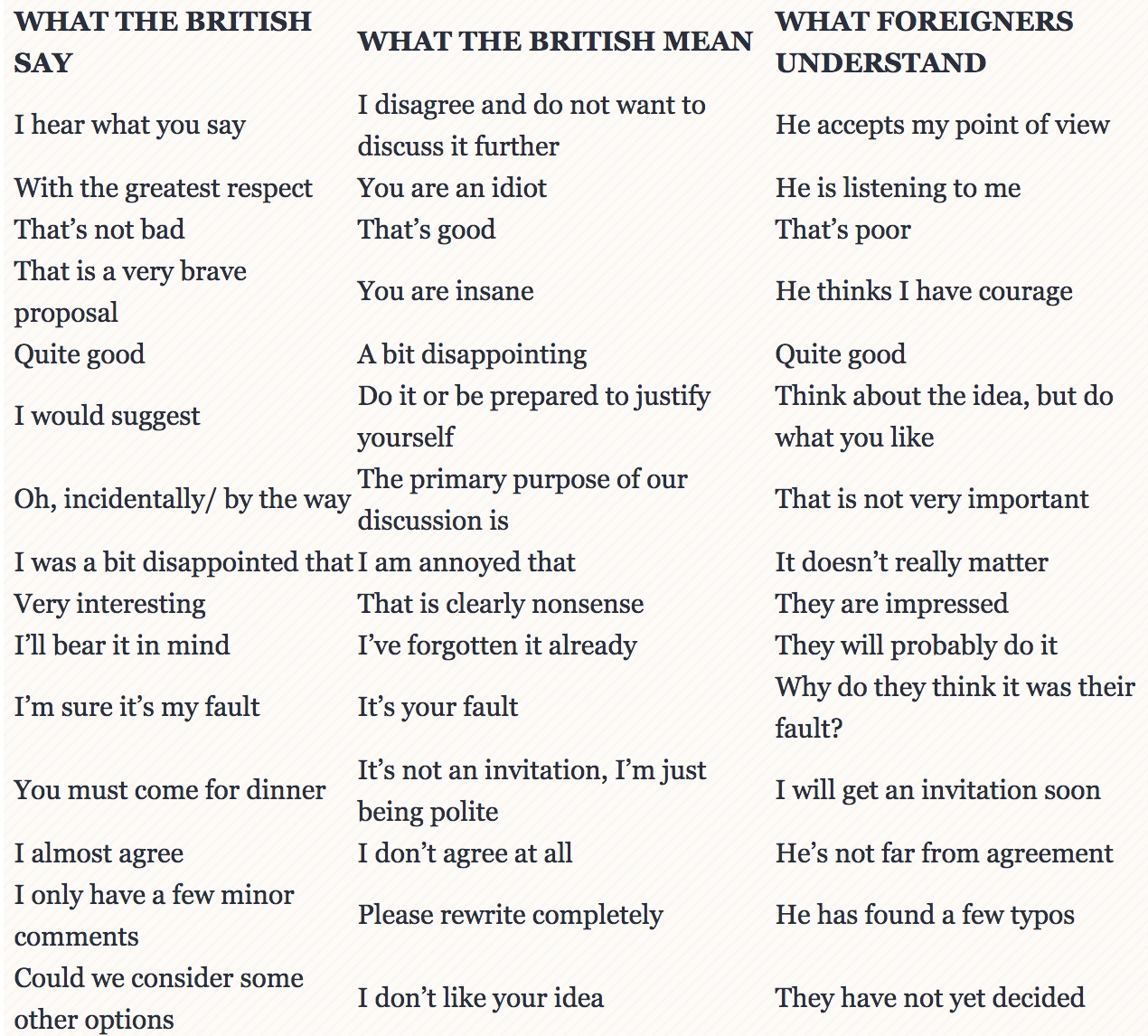
Last week marked the end of this year’s Masterchef competition in the UK. Once again our family sat, drooled and marvelled at the creations of Simon Wood, this year’s winner. His combination of ingredients, skills, techniques and presentation was outstanding, and from the minute the camera zoomed in on his final three courses, you know that you had seen what good looks like.
For his starter he cooked octopus served with chorizo crisps, cannellini beans and chorizo salad, brunoise tomatoes and a sherry and smoked paprika vinaigrette. His main course was squab pigeon served two ways — roasted breast, and a pigeon leg bon-bon, stuffed with pigeon leg meat, chicken, mushroom duxelle and Armagnac — served with three types of heritage carrots, pommes parisienne, girolle and trumpet mushrooms, carrot puree, watercress puree and a cassis jus. For pudding he whipped up a lemon posset topped with citrus tutti-frutti - charred grapefruit and orange, a lime tuile and limoncello — topped with pistachio crumb, edible flowers, tarragon leaves and a lime air. Mmmm.
When it comes to organisations, with such a wide range of available knowledge-related ingredients, tools and techniques which can have a potential impact, it can difficult to discern "what good looks like" and which ingredients should be given prominence at different times. But that shouldn't stop us trying!
Here's my attempt to describe what it good looks like when it comes to knowledge management...
Leadership. Leaders in the organisation are collaborative role models, challenging people to ask for help, seek out, share and apply good practices. This inspires curiosity and a commitment to improve.
Collaboration. People have the desire and capability to use work collaboratively, using a variety of technology tools with confidence. Collaboration is a natural act, whether spontaneous or scheduled. People work with an awareness of their colleagues’ availability and expertise and use collaboration tools as instinctively as the telephone to increase their productivity.
Learning. People instinctively seek to learn before doing. Lessons from successes and failures are drawn out in an effective manner and shared openly with others who are genuinely eager to learn, apply and improve. Lessons lead to actions and improvement. Project and programme management create a healthy supply and demand for knowledge, and can demonstrate the value it creates.
Networking. People are actively networking, seamlessly participating in formal communities and harnessing informal social networks to get help, share solutions, lessons and good practices. The boundaries between internal and external networks are blurred and all employees understand the benefits and take personal responsibility for managing the risks.
Navigation. There are no unnecessary barriers to information, which is shared by default and restricted only where necessary. Information management tools and protocols are intuitive, simple and well understood by everybody. This results in a navigable, searchable, intelligently tagged and appropriately classified asset for the whole organisation, with secure access for trusted partners.
Embedding. Knowledge management is fully embedded in people management and development, influencing recruitment and selection. Knowledge-sharing behaviours are built-into induction programmes and are evident in corporate values and individual competencies. Knowledge transfer is part of the strategic agenda for HR. The risks of knowledge loss are addressed proactively. Knowledge salvage efforts during hurried exit interviews are a thing of the past!
Consolidation. People know which knowledge is strategically important, and treat it as an asset. Relevant lessons and practival recommendations are drawn from the experience of many, and consolidated into guidelines. These are brought to life with stories and narrative, useful documents and templates and links to individuals with experience and expertise. These living “knowledge assets” are refreshed and updated regularly by a community of practitioners.
Social Media. Everybody understands how to get the best from the available tools and channels. Social media is just part of business as usual; people have stopped making a distinction. Serendipity, authenticity and customer intimacy are increasing. People are no longer tentative and are encouraged to innovate and experiment. The old dogs have learned new tricks! Policies are supportive and constantly evolving, keeping pace with innovation in the industry.
Storytelling. Stories are told, stories are listened to, stories are re-told and experience is shared. People know how to use the influencing power of storytelling. Narrative is valued, captured, analysed and used to identify emergent patterns that inform current practice and future strategy.
Environment. The physical workplace reflects a culture of openness and collaboration. Everyone feels part of what’s going on in the office. Informal and formal meetings are easily arranged without space constraints and technology is always on hand to enhance productivity and involve participants who can’t be there in person.
How's that for some food for thought?